The individual income tax shall be paid by the income earner, i.e. the individual who has the direct tax obligation according to the tax law.
Taxpayers are divided into resident individuals and non-resident individuals, who bear different tax obligations. An individual who is domiciled in China, or an individual who is not domiciled in China but has resided in China for an aggregate of 183 days or more within a tax year, shall be regarded as a resident individual. Income received by a resident individual from within China or overseas shall be subject to individual income tax. However, if an individual who is not domiciled in China has resided in China for less than six consecutive years during which he or she has resided for an aggregate of 183 days or more every year, he or she is exempt from individual income tax on income derived from outside China and paid by an entity or individual outside China, upon filing with the competent tax authority.
An individual who is not domiciled in China and does not reside in China, or an individual who is not domiciled in China but has resided in China for less than an accumulated 183 days within a tax year, shall be regarded as a nonresident individual. Income received by a non-resident individual from within China shall be subject to individual income tax. However, if an individual who is not domiciled in China resides in China for not more than 90 days in a tax year, the portion of his or her income derived from within China that is paid by an overseas employer and is not borne by this employer's institution or site in China is exempt from individual income tax.
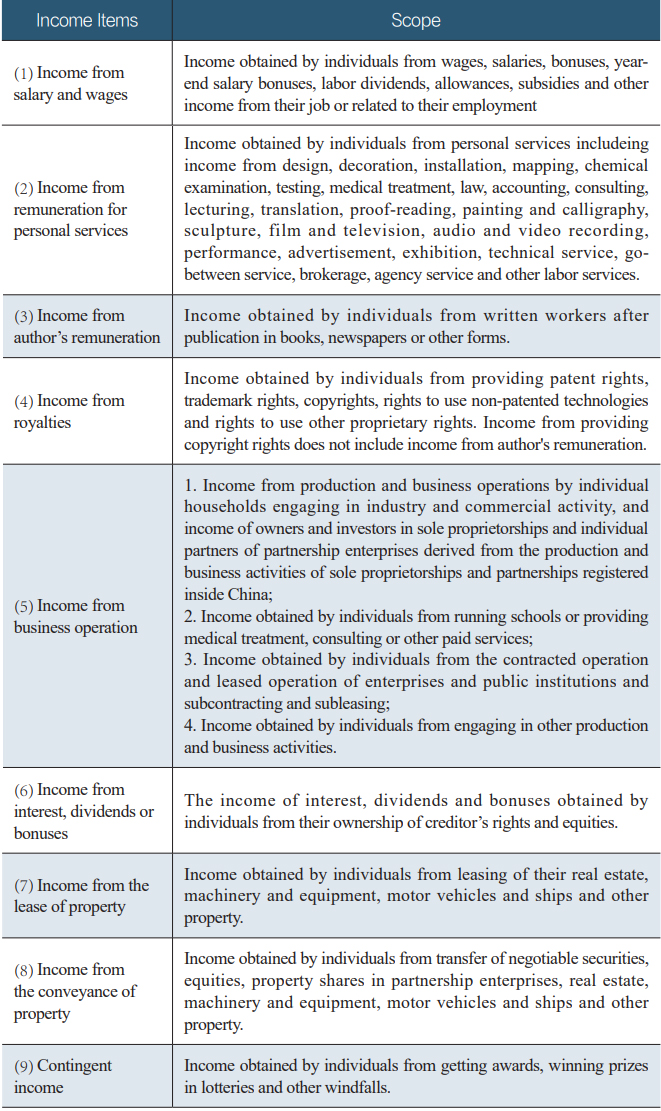
(I) Incomes subject to individual income tax
Individual Income Tax Law and its Implementation Regulations stipulate the nine forms of income and the corresponding scope of individual income tax. Individuals shall calculate and pay individual income tax according to the corresponding requirements when they obtain these incomes.
Table 1 Scope of Income Items
(II) Individual Income Tax Rates
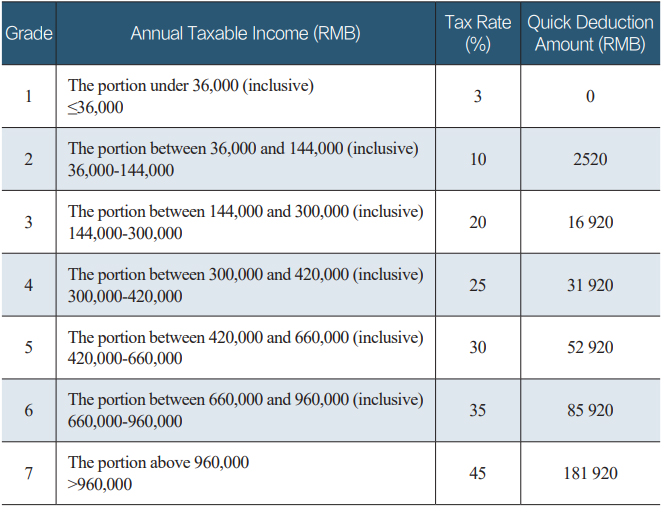
In China, different taxable income items are subject to different individual income tax rates. 1. The seven-grade progressive tax rates in excess of specific amount ranging from 3% to 45% are applicable for comprehensive income.
(applicable to resident individuals)
(applicable to non-resident individuals)
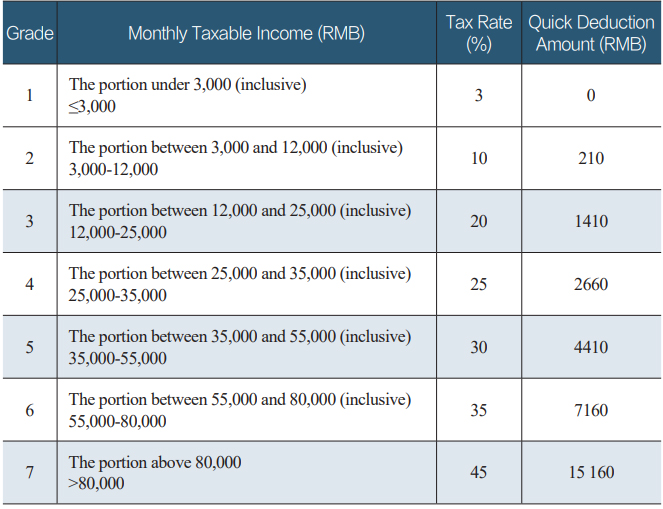
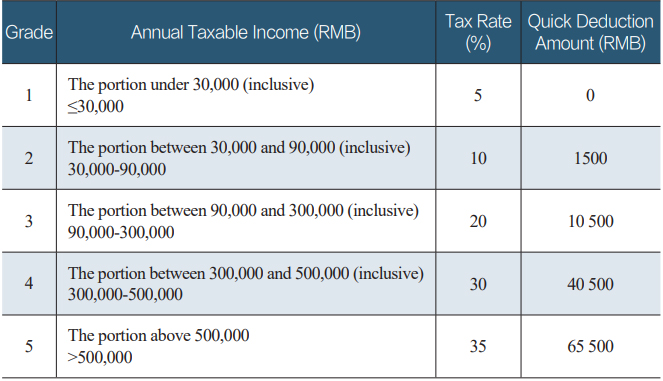
Table 4 Tax Rates for Income from Business Operation
(III) Tax benefits for foreigners
1. Tax exemptions for foreign individuals' allowances and subsidies
The following allowances and subsidies obtained by foreign individuals (including Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan compatriots) are exempted from personal income tax presently:
(1) Housing subsidies, food allowances, moving fees and laundry fees gained by foreign individuals in the non-cash form or in the form of being reimbursed for what they spend;
(2) Relocation expenses obtained in the form of actual reimbursement for actual costs in connection with employment or dis-employment in China, excluding monthly or regular payments made by the employer to the foreign employee in the name of relocation expenses;
(3) Allowances for business travelling at home and abroad gained with reasonable standards;
(4) Family visiting expense within a reasonable amount, which is deffned as only the cost of transportation between the individual's place of employment in China and his or her home location (including the residence of spouse or parents) for not more than twice a year;
(5) The portion of language training fees and children's education fees occurred in China that is considered reasonable;

Starting from January 1, 2004, with regard to the foreign individuals hired by enterprises within China (excluding individual residents of Hong Kong or Macao) who live in Hong Kong or Macao for family or any other reason, come and go between the Mainland and Hong Kong or Macao, the housing, food, laundry and move subsidies given to them by the enterprises within China (including their connected enterprises) in non-cash form or in the form of actual reimbursement for actual costs may, if supported by valid voucher, and upon examination and confirmation of the competent tax organ, be exempted. With respect to the subsidies obtained by any of the foreign individuals as mentioned above for the expenses of his (her) language training and children education in Hong Kong or Macao, if they can provide valid payment voucher and other materials, the subsidies determined as reasonable by the competent tax organ upon examination and confirmation shall be exempted from the individual income tax.
From January 1, 2019 to December 31, 2021, foreign individuals who meet the criteria of resident individuals can enjoy the special additional deduction of personal income tax; or according to the provisions of the preferential tax policies, they can enjoy the subsidies and tax exemptions such as housing allowance, language training fees, children’s education fees. They can choose to enjoy either of the above two policies. Once selected, it cannot be changed within a tax year. From January 1, 2022, foreign individuals will no longer enjoy subsidies and tax exemptions such as housing allowance, language training fees, children’s education fees, and shall enjoy special additional deductions in accordance with the regulations.
2. Lump sums paid by foreign employers
For foreign staff coming to China with a lump sum paid by their foreign employers, which includes personal salary, public expenses (postage, office expenses, advertising expenses, necessary social expenses for business operations), living allowance (housing expenses, travel expenses), where the above-mentioned incomes can be clearly classiffed, then only income obtained from salary and wages is subject to individual income tax in accordance with the regulations.
3. Tax beneffts for dividends
The incomes gained by individual foreigners (including Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan compatriots) from dividends and bonuses of foreigninvested enterprises are exempted from individual income tax.
4. Tax exemptions for foreign experts’ wage and salary income
The wage and salary incomes gained by foreign experts (including Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan compatriots) who conform with one of the following conditions may be exempt from individual income tax:
(1) Foreign experts directly sent by the World Bank to work in China in accordance with a special loan agreement;
(2) Experts directly sent by the United Nations’ Organizations to work in China;
(3) Experts coming to work in China for the UN aid projects;
(4) Experts sent by an aid-granting country to China to work specially for the project granted gratis by the country;
(5) Cultural and educational experts coming to China to work for up to two years on the cultural exchange project under an agreement signed between two governments, with their wages and salaries being borne by the country concerned;
(6) Cultural and educational experts coming to China to work for up to two years on the international exchange projects of China’s universities and colleges, with their wages and salaries being borne by the country concerned;
(7) Experts coming to work in China through a non-government scientiffc research agreement, with their wages and salaries being borne by the government organization of the country concerned.
5. Tax exemptions for income from stock transfer
Starting from November 17, 2014, the income of individual investors in the Hong Kong market derived from the transfer difference obtained from investing in A shares listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange is temporarily exempted from individual income tax; Starting from December 5, 2016, the income of individual investors in the Hong Kong market derived from the transfer difference obtained from investing in A shares listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange is temporarily exempted from individual income tax.
Starting from December 18, 2015, the income of individual investors in the Hong Kong market derived from the transfer difference between the shares of Chinese mainland funds bought and sold through mutual recognition of funds is temporarily exempted from individual income tax.
(IV) Declaration methods of individual income tax
Table 5 Declaration Methods
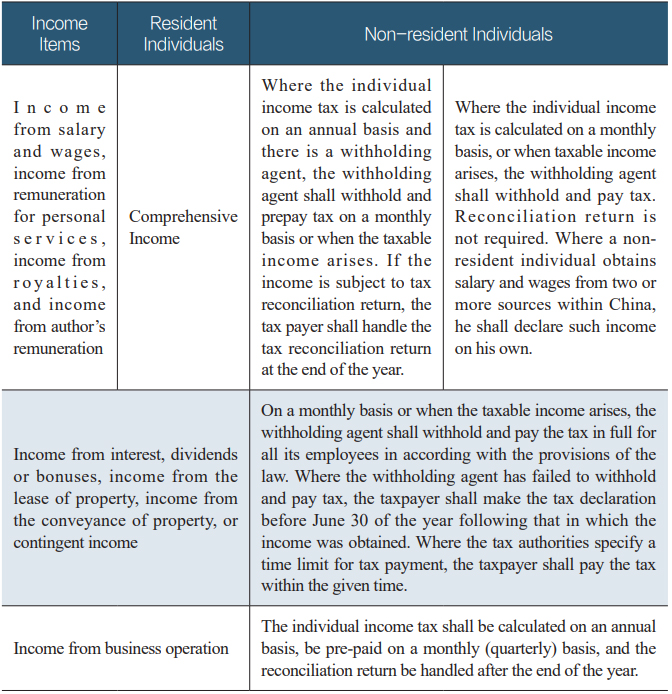
1. Where the taxpayer obtains comprehensive income for which the annual tax reconciliation return is required;
2. Where the taxpayer obtains taxable income but there is no withholding agent;
3. Where the taxpayer obtains taxable income but the withholding agents has failed to withhold and pay the tax;
4. Where the taxpayer obtains income from overseas;
5. Where the taxpayer emigrates to another country and cancels his Chinese household registration;
6. Where a non-resident individual obtains salary and wages from two or more sources within China;
Taxpayers can use the mobile APP for individual income tax or the WEB terminal of the Electronic Tax Bureau for Natural Persons to make the declaration, or use postal declaration, or visit the tax service center to handle the declaration.
Source: Guide For Foreigners In Guangzhou(2021)





 京公网安备
京公网安备